Eat your Vitamins
(this section is a work in progress…)
more information coming soon…
Vitamin A
Our bodies can make Vitamin A from beta carotene so eating foods with beta carotene and eating foods with Vitamin A are both ways to increase your Vitamin A intake.
Foods with Vitamin A - Eggs, some Fish
Foods with beta carotene - Carrots, Sweet potato, Squash, Cantaloupe, Tomato, Spinach, Kale, Broccoli
Vitamin A is important for vision, skin health, and immune system functioning.
Our bodies turn Vitamin A into several metabolites - Retinol, Retinal, Retinoic acid - these are used to help with our vision, skin health, and immune system activity.
Vision - Rhodopsin is made from these metabolites of Vitamin A. Rhodopsin is a photopigment in our Retina that helps our eyes adjust to dim light - which helps us see at night.
Skin health - Retinoic acid helps with cell differentiation/ maturation/ turnover. Many cells in our body are regularly replaced by new cells. In our skin, this helps with wound healing. This also helps our immune system because our skin and mucous membranes are our first line of defense against bacteria. If our skin and mucous membranes are healthy and their cell borders are tight, this prevents bacteria from getting through into our bodies.
Immunity - Retinoic acid is used to make T-lymphocytes, which are one of the types of white blood cells that fights infection.
So eat your eggs, fish, carrots, sweet potato, squash, cantaloupe, tomato, spinach, kale, and broccoli for your vision, skin health, and immune system!
B Vitamins
Apples, Almonds, Asparagus, Avocados, Bananas, Beans, Blueberries, Broccoli, Brussel sprouts, Butternut squash, Cantaloupe, Cherries, Chia seeds, Chick peas, Dairy products- milk, cheese, yogurt, Edamame, Eggs, Fish, Whole grains, Grapes, Grapefruit, Green onion, Green peas, Honeydew, Jalepeno, Kale, Kiwi, Legumes, Lemon, Lentils, Romaine lettuce, Mango, Oranges, Papayas, Passion fruit, Peanuts, Pecans, Pine nuts, Pineapple, Pinto beans, Pistachios, Pork, Poultry, Raspberries, Red bel pepper, Red meat/beef, Red onion, Brown rice, Salmon, Seafood/ Shellfish, Spaghetti spinach, Squash, Strawberries, Sunflower seeds, Sweet potato, Tomato, Tuna, Turnip greens, Walnuts, and Yogurt
B Vitamins are COENZYMES. Coenzymes enhance the hundreds of chemical reactions happening in your body. This helps your body’s chemistry and metabolism work faster and more efficiently.
-Alcohol inhibits the functioning of B Vitamins.
-Vitamin C helps with the absorption of some B Vitamins.
-Some B vitamins activate other B vitamins which is why eating a wide variety of foods is important.
B Vitamins help to break down the foods that you eat, releasing ENERGY from carbohydrates and fats and proteins, and building amino acids and hormones.
B Vitamins help with cell division and tissue growth, which makes them important in cells with high turnover, such as in the blood, gut, skin, hair, and nails.
Some B Vitamins help to make NEUROTRANSMITTERS - the chemicals in the brain that affect our mood. They are also used to make myelin sheaths - these insulate our nerves and increase NERVE FUNCTION efficiency.
Some B vitamins are important for IMMUNITY, and help to make red and white blood cells.
Some B vitamins serve as ANTIOXIDANTS. They break down homocysteine and also detoxify metals in the body.
Some B vitamins help with DIGESTION and muscle tone in the GI tract. There are neurotransmitters in the GI tract and B Vitamins help to build these as well.
Some B vitamins help with muscle tone in the HEART for proper functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Some B Vitamins are involved in a chemical process called methylation. METHYLATION promotes healthy mental and physical activity. Methylation regulates gene expression and protein function. Methylation also influences the functioning of the nervous, cardiovascular, and immune systems and helps with energy production, heavy-metal detoxification, and hormone balance.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C / Ascorbic acid:
Apple, Avocado, Banana, Bell peppers, Boy Choy, Broccoli, Brussel Sprouts, Cabbage, Cantaloupe and other melons, Cauliflower, Cherries, Chia seeds, Cucumber, Grapefruit, Green Onion, Green Peas, Guava Fruit, Jalepeno, Kale, Kiwi, Lemons, Limes, Mango, Okra, Oranges, Papaya, Pears, Peppers, Pistachios, Pomegranate seeds, Potato/ Sweet potato, Radishes, Raspberries, Red Onion, Salmon, Shallots, Spinach, Strawberries, Squash, Tomato, Greek Yogurt, Zucchini
-ANTIOXIDANT (protects cell membranes against damage, important in eye health, immunity)
-Recycles Vitamin E so that it can be re-used by our cells (Vitamin E is also an antioxidant)
-IMMUNITY (used by cells in the immune system, important for chemical reactions and cell signaling that occur in the immune system)
-is important for the absorption of IRON (transforms iron into its absorbable form, also involved in the cycle of iron storage as Ferritin)
-is an enzyme Cofactor (enables enzymes to function more efficiently, which facilitates many cellular functions)
-is involved in the chemical reaction which is necessary for Collagen synthesis (Hydroxylation reaction), collagen is important in wound healing and overall skin health, Collagen is also in Bones, Blood vessels, and Hair
-is used to build Cartilage, Bone, and Teeth (Fibroblast and Osteoblast cells use vitamin C)
-is involved in the chemical reaction which is necessary for the production of Norepinephrine and Serotonin (Hydroxylation reactions)
-helps to build Carnitine, which is used to get Fat through cell membranes, so that fat can be broken down and used for energy in cells
-activates Folate (folate is used to build RNA and DNA and Proteins)
Vitamin D
Vitamin D receptors are found throughout the body (research is still being conducted to determine its function in many parts of the body)
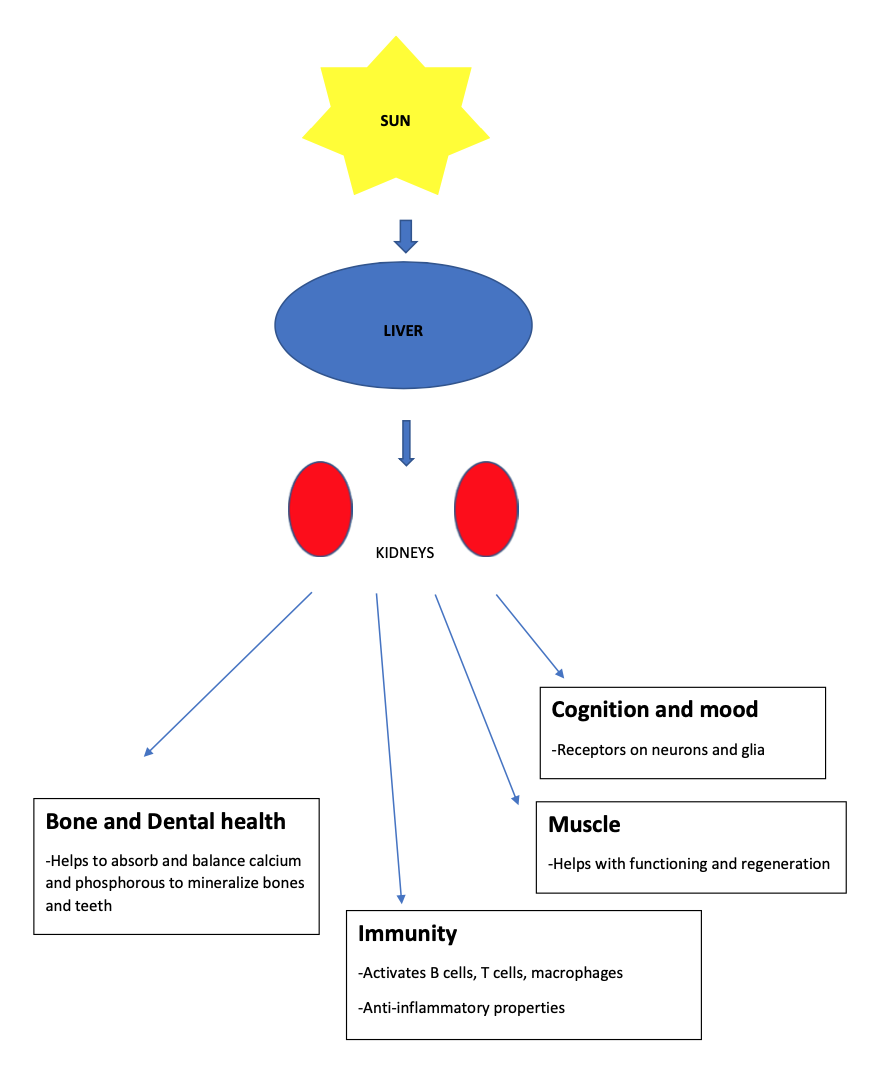
Vitamin D is made when uv light is absorbed through our skin from the Sun, it is then activated in the Liver, and further activated in the Kidneys
-Bone and Dental health- Mineralization of bone, Absorption of Calcium and Phosphorous, Maintains the balance between calcium and phosphorous needed for healthy bones and teeth
-Involved in Blood Glucose control- Regulates beta cell function, the beta cells of the Pancreas release insulin into the bloodstream to keep our sugar levels down
-Involved in Cognitive function and Mood- with receptors on neurons and glia in the areas of the brain involved in the pathophysiology of depression
-Affects Skeletal Muscle function, believed to play a role in muscle regeneration
-Supports Immune health, Activates various parts of the immune system including B cells, T cells, and Macrophages, Also has anti-inflammatory properties
Sources- fortified foods/ milk/ juices, fish oils, salmon and tuna, cheese, mushrooms, egg yolks, sunlight, (supplements)**This may be one of the only supplements that most people need, because it is difficult to safely obtain enough vitD from the sun and it is in a pretty low concentration in foods
Vitamin E
- Vitamin E is an anti-oxidant.
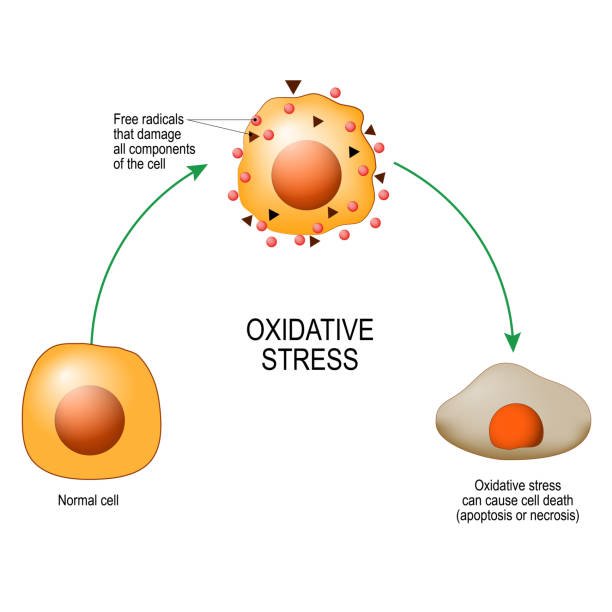
- Antioxidants help to protect cells from damage by free radicals.
- Free radicals are loose electrons that damage cells and their membranes.
Sources of Free Radicals:
*By-product of normal chemical/metabolic reactions/processes occurring in the human body
*External sources- uv light, cigarette smoke, air pollutants, pesticides...
*Food sources- foods high in refined sugar and carbohydrates, Processed Meats (due to the preservatives), Red Meat, and Alcohol
Antioxidants break down free radicals. This process protects cell membranes, stabilizes cholesterol to help prevent damage to the heart and blood vessels, and protects skin against oxidative damage. Antioxidants may also protect against environmental pollutants in the lungs and may stabilize DNA.
Vitamin E is one of several antioxidants. It is found in cell membranes. When free radicals approach cell membranes, Vitamin E comes out of the cells and binds these free radicals/loose electrons to prevent cell membrane damage.
Vitamin C is able to recycle Vitamin E, removing the negative charge caused by the free radical, to allow Vitamin E to continue to protect against additional free radicals as they approach the cell.
Vitamin E improves immunity by protecting cell membranes and protecting red and white blood cells from oxidation/damage by free radicals.
Sources - Sunflower seeds, Almonds, Hazelnuts, Pine nuts, Brazil nuts, Peanuts, Peanut butter, Spinach, Swiss chard, Turnip and Collard and Mustard greens, Butternut squash, Pumpkin, Sweet potato, Olive oil, Red bell pepper, Asparagus, Avocado, Broccoli, Kiwi, Blackberries, Mango, Salmon, Trout, Shrimp
**heating can reduce the antioxidant properties of Vitamin E so pour olive oil over cooked foods and eat some raw nuts
Vitamin K
There are 2 forms of Vitamin K
1. One form is found in vegetables
2. The other form is found in animal products and fermented foods. This 2nd type of Vitamin K is also produced by the bacteria in our gut, so this is one of the many reasons to keep your gut bacteria healthy and functioning optimally.
Through a carboxylation reaction, Vitamin K activates many enzymes/proteins within the body:
-Osteocalcin- important in bone metabolism
-Enzymes involved in cell signaling and cell function
-Blood clotting enzymes
****Some anticoagulant medications can be affected by Vitamin K levels so talk to your doctor before consuming more of these foods if you are on these medicines****
Sources - Asparagus, Broccoli, Brussel sprouts, Cabbage, Carrots, Cauliflower, Collard greens, Green beans, Kale, Lettuce, Soybeans, Spinach, Turnip greens, Cheese, Eggs, Kimchi, Sauerkraut
Eat these foods for:
** Stronger BONES/TEETH
** Healthier blood CLOTTING
** More efficient CELL functioning